- Can Sound Kill You
1.1 What Is Noise Pollution
1.2 How Does Noise Pollution Impact Our Health - How Much Sound Can Kill You
2.1 When Loud Becomes Dangerous
2.2 How Loud Does A Noise Have To Be To Kill - How Does Sound Kill You
3.1 The Damage Noise Can Cause - Sounds That Can Kill You On The Spot
4.1 Are There Acoustic Weapons
4.2 How Much Of This Is Science Fiction - How to Protect Yourself From Dangerous Sounds
- Measure The Sound Level With Decibel Pro App
You’ve probably seen lethal sound weapons in spy and sci-fi movies. But how real are they? Is the idea that sound can kill you just myth or could it be real?
In this article, we’re going to separate fact from fiction: can sound waves kill you? Read on to find out.
Can Sound Kill You?
The question ‘Can sound kill you has a simple and straight answer. Yes, it can! Sound can kill you in multiple ways.
If we’re talking about sounds within the human hearing frequency range (between 20 and 20,000 Hz), high-intensity sounds above 150 decibels can burst your eardrums, while sounds above 185 dB can impact your inner organs and cause death. They can do this by causing an air embolism in your lungs, affect inner organs, or even make your lungs explode. However, to instantly kill, a sound would have to be as loud as 240 dB which is hard to come by.
Certain infrasound frequencies can also be potentially lethal.
What Is Noise Pollution
Noise pollution (or environmental noise) represents loud noise levels that can impact human health. Prolonged or constant exposure can affect our wellbeing. In modern society, this noise is caused by devices, transport, machinery, construction, or sound propagation systems.
Large cities are most prone to noise pollution because they are high-density areas where many noisy activities are carried out in the course of everyday life. The World Health Organization estimates that the average noise level in our cities is 95 dB. This is much higher than the recommended noise level of 50 dB that the same organization has set for residential areas.
How Does Noise Pollution Impact Our Health
Noise pollution has many adverse effects on human health. From the obvious potential hearing damage and gradual or permanent hearing loss, noise pollution can also affect our overall and mental wellbeing.
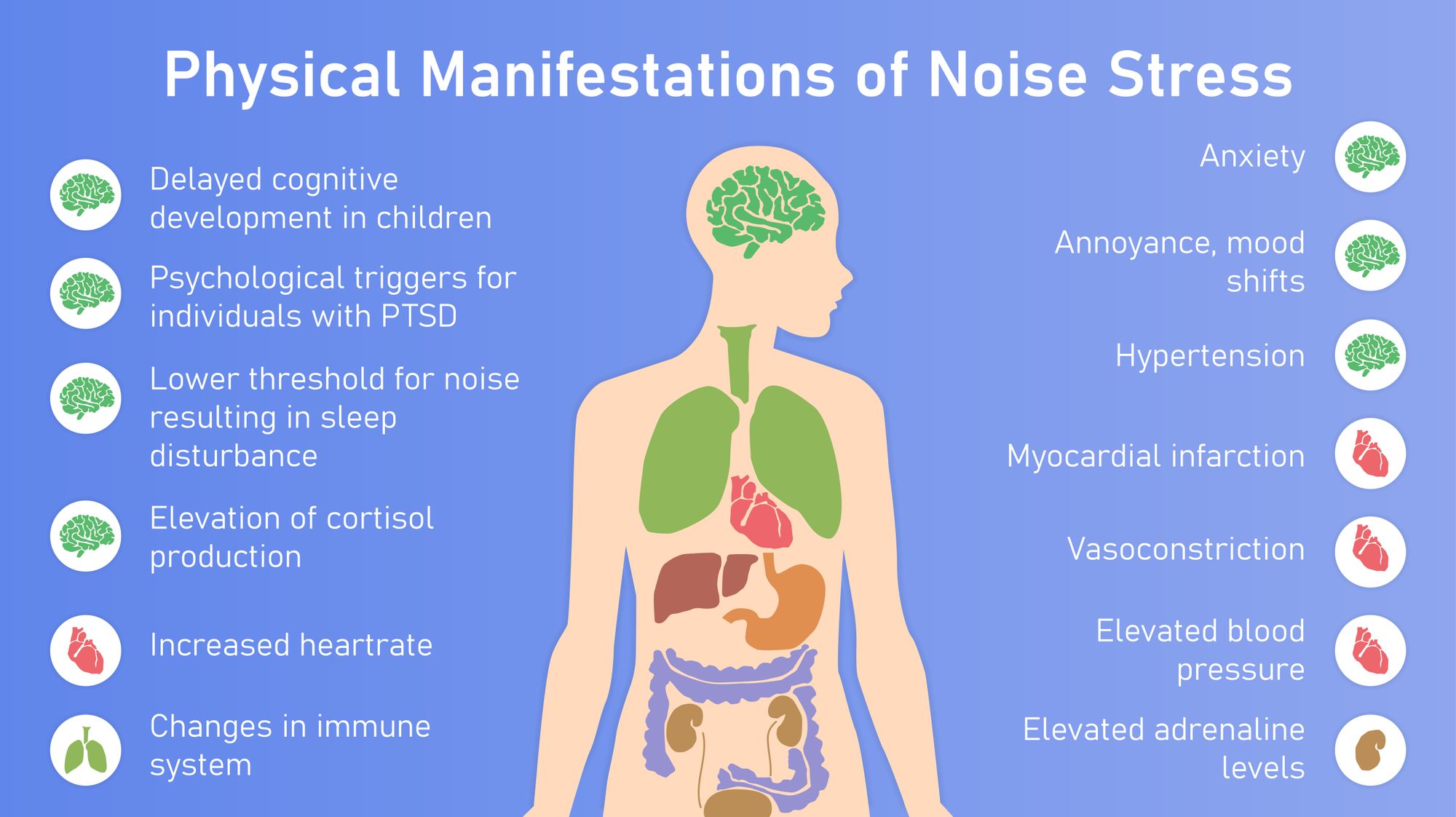
Noise pollution can cause:
- cardiovascular disorders
- coronary artery disease
- hypertension
- increased stress levels
- tinnitus
- sleep disturbance
- faster cognitive decline
- learning and behavior issues-particularly in children
How Much Sound Can Kill You?
Sounds are pressure waves that are picked up by our ears and cause our eardrums to vibrate. A loud sound can build up enough pressure to cause the eardrum or even internal organs to rupture or explode.
Sounds above 150 dB have the potential of causing life-threatening issues. Sounds between 170-200 dB are so intense that they can cause lethal issues like pulmonary embolisms, pulmonary contusions, or even burst lungs. As for exploding heads, you can expect that from sounds above 240 dB.
However, such high intensity sounds are very rare. Imagine a loud rock concert and double or triple that noise level to imagine how loud a sound that can kill you would be.
In general, sounds levels above 150 dB are produced by rare events like massive explosions or rocket launches.
When Loud Becomes Dangerous
Sound can become dangerous to humans when it exceeds 85 dB. That is considered the limit from which loud noise can cause hearing damage. Prolonged exposure (over 8 hours per day) to this level is believed to cause hearing loss. You should avoid exposure to noise levels above 85 dB or wear hearing protection when you cannot.
However, even sound levels below 85 decibels can be harmful. According to WHO, noise levels above 50 dB can cause sleep disturbance, affect learning and thinking abilities and diminish a person’s quality of life.
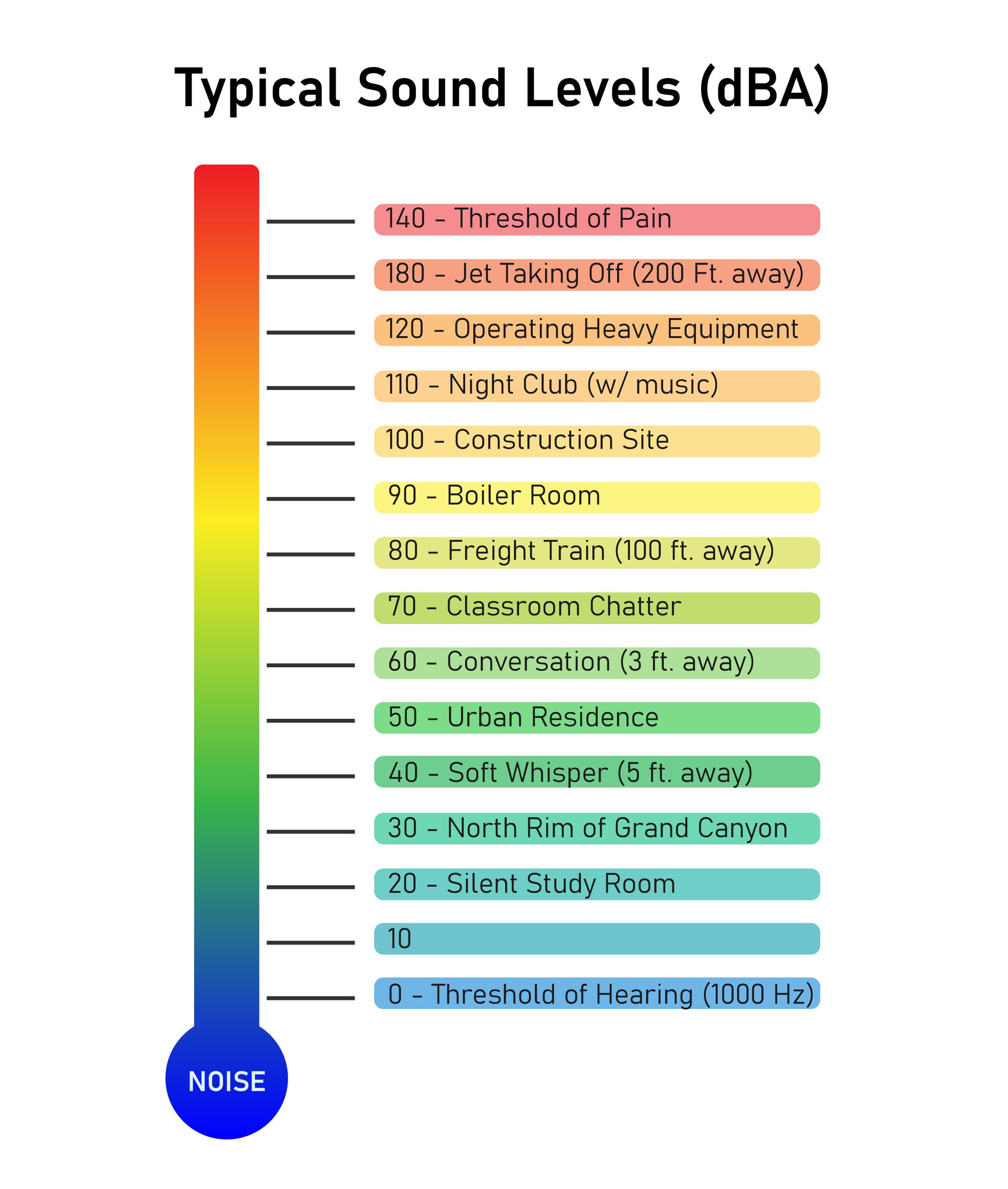
As for noise levels above 85 dB, the threshold of pain (caused by loud noise) is at 140 dB and sounds above 150 dB can affect your eardrums as well as internal organs.
Some believe total silence can also be harmful. The quietest place on Earth, an anechoic chamber is said to make a person go crazy in less than 30 minutes.
How Loud Does a Noise Have To Be To Kill?
In the case of sounds we can hear, to actually kill you, scientists believe that loud a sound must exceed 185 or even 200 dB.
From 150 dB on, sounds can start affecting your inner ear and then your inner organs. In such cases, sound can cause life-threatening internal injuries and even death.
In the case of sounds we cannot hear, which are below or above the human frequency range, things are a little more complicated. Humans cannot hear sounds below 20 Hz or above 20,000 Hz because when sound waves travel too slowly or too quickly, our body can’t translate that motion into signals our brains understand.
Therefore, it is possible for a sound to be extremely loud and for you not to hear it but be affected by it. The low pitch sounds in particular can travel much farther than higher frequencies and affect our wellbeing or even kill us.
How Does Sound Kill You?
Sound is a wave of pressure that acts just like an actual wave. It can move through both solids and liquids and pass through our bodies as well.
If the pressure buildup is high enough, it can cause damage to our eardrums and internal organs.
The Damage Noise Can Cause
Loud noise (above 55 dB) can cause non-life-threatening issues such as:
- loss of focus
- diminished learning abilities
- increased stress levels
- sleep disturbance
Loud noise above 85 dB can cause:
- tinnitus
- hearing damage
- hearing loss
- increased blood pressure levels
- cardiovascular issues
Loud noise above 150 dB can cause:
- eardrum ruptures
- pulmonary contusions
- embolisms
Infrasound or low-frequency noise (below 20 Hz) can cause:
- blurred vision
- erratic breathing
- joint issues
- nausea
- visual impairment
- inner organ damage
7 Hz infrasound (the frequency of the brain and the internal organs) can affect the human central nervous system and cause:
- general confusion
- anxiety and panic
- bowel spasms
- nausea and vomiting
- organ rupture
- death (in cases of prolonged exposure)
Sounds That Can Kill You On The Spot
Here are a few of the sounds that can kill you:
- sounds above 185 dB (loud explosions, rocket launches)
- infrasound especially at 7 Hz
Are There Acoustic Weapons?
The only known acoustic weapon ever used was the “Luftkanon” or “Wirbelwind Kanonew”. It was used by the German military in World War II to bring down enemy aircraft using a vortex of sound. However, this acoustic weapon was not very successful.
The only acoustic weapon known to be in use is the Long-Range Acoustic Device (LRAD). It is a sound cannon with an extremely high decibel capacity used for crowd control.
Other acoustic weapons that can incapacitate, injure, or even kill are being researched or developed by some military forces. Some use loud sound, while some use ultrasound or infrasound.
These acoustic weapons can include:
- sonic bullets
- acoustic grenades
- sonic mines
- sonic cannons
How Much Of This Is Science Fiction?
Acoustic weapons were popular among military researchers during and after World War II. One example is the experiments of Vladimir Gavreau in the late 1950s. He was looking into low-frequency sound to create an acoustic weapon for the French military. Unfortunately, it nearly caused the death of his researchers and himself because it made their hearts, lungs, and stomachs vibrate so hard and was never completed.
Apart from the LRAD, the crowd-control device, there are no other acoustic weapons known to be still in use. Nevertheless, some research into sonic weapons is still ongoing and some smaller-scale weapons or tactics are believed to be used in interrogations.
More recently, the American Electronics Corporation (AEC) announced that it has developed a non-lethal sound cannon for the Pentagon. It directs painful or disturbing ultrasonic sounds towards a target and can incapacitate a person at up to 30 m.
How To Protect Yourself From Dangerous Sounds
It’s important to be aware of the noise level in your surrounding environment to keep your hearing and overall health safe. A sound measurement tool like a sound level meter or a sound level meter app can be very useful in monitoring and controlling unwanted noise exposure.
To protect yourself from dangerous noise, you should:
- monitor noise levels at home and at your workplace
- avoid noise levels above 85 dB as much as possible
- wear hearing protection or move away from the source when you cannot avoid exposure
- turn down the volume on your headphones (keep it at 60% and take regular breaks)
Measure The Sound Level with Decibel Pro App
Decibel Pro is a professionally calibrated sound-level app that’s easily downloadable on any iPhone or iPad. Use it to get instant noise level measurements and monitor the noise levels you are exposed to every day.
You can also use Decibel Pro to test your hearing and identify any hearing sensitivity or damage early on.
To learn more about the Decibel app, click here.



