- What Is The Decibel Level Of The Noise In A Typical Classroom
1.1 The lowest level
1.2 The highest level
1.3 Average noise level - The Main Sources Of Noise At School
2.1 Equipment
2.2 Reverberation
2.3 Neighboring classrooms and hallways
2.4 Lighting
2.5 HVAC - Background Noise In Classrooms
3.1 Signal to noise ratio (SNR) - Recommendations For Noise Prevention In Classrooms
- Test Your DL Of The Noise In A Typical Classroom With Decibel Pro App
Ever wondered what is the decibel level of noise in a typical classroom? It may be much higher than you think. And it may lead to study and focusing difficulties, as well as hearing health issues.
In this article, we’re taking a closer look at what the decibel level of the noise in a typical classroom is, what the level should be, and what we can do to protect children from dangerous noise levels.
What Is the Decibel Level of the Noise in a Typical Classroom?
As you would expect, the decibel level of noise in a typical classroom is not universal. There are many elements that contribute to how loud a classroom is.
For one, there is the number of students. An empty classroom will be much quieter than a classroom full of students. Then, there is the type of room. Softer rooms have sound-absorbing walls or floors, ceilings, or walls made of or covered in other absorptive materials.
So, to answer the question ‘What is the decibel level of the noise in a typical classroom?’, let’s consider the lowest and the highest levels, as well as the average:
The Lowest Level
In the US, the American National Standard for Acoustical Performance Criteria, Design Requirements, and Guidelines for Schools, or ANSI S12.60 for short, requires unoccupied classrooms to have background noise of 35 dBA. The World Health Organization recommends the same level of 35 decibels (A-weighted) as safe.
The ANSI S12.60 standard considers a standard classroom to be less than 10,000 cu ft, with a 0.6 sec. reverberation time, and a signal-to-noise ratio of 15 dBA.
If we consider this lowest level of noise for a classroom of 35 dBA and the fact that the human voice is between 50 and 70 dBA, this means that the teacher’s voice needs to be at 50 dBA to be heard by the students.
The Highest Level
As for the highest decibel level of noise in a typical classroom, it can be much higher than you would expect.
A full classroom of children playing or talking at the same time can reach decibel levels up to 95 dBA. Considering that the OSHA (the US Occupational Safety and Health Organization) permissible exposure limit is 90 dBA over an 8-hour day, levels above 90 decibels in schools can become very problematic.
In fact, kids being exposed to loud noise for hours each day can lead to:
- Difficulty understanding what the teacher is saying in classes
- Difficulties focusing and learning in class
- Discomfort (feeling uncomfortable) and increased levels of stress
- Tinnitus or hearing issues
Average Noise Level
Considering an average is the best way to determine what the decibel level of the noise in a typical classroom is. According to multiple studies, the average noise level of an occupied classroom is 48 dBA when there is less activity going on and above 60 dBA when the children are engaged in activities such as playing, talking, or doing group work.
Here are some examples of measured background noise:
- Over 15 pupils engaged in group work in an ordinary classroom - 45-50 dB
- 11 unruly students doing group work - 60-65 dB
- 2 children arguing over toys - 78-82 dB
- School break bell in the hallway (measured 2 meters away) - 115 dB
- Music class with students talking - 68-73 dB
- School kitchen (including background noise from machinery) - 67-80 dB
- Woodworking shop (with background noise from power tools) - 78-90 dB
The Main Sources of Noise at School
When determining the decibel level of noise in a typical classroom, we need to take into account inside and outside noise.
There are numerous sources of noise at a school as you can see in the graphic below:
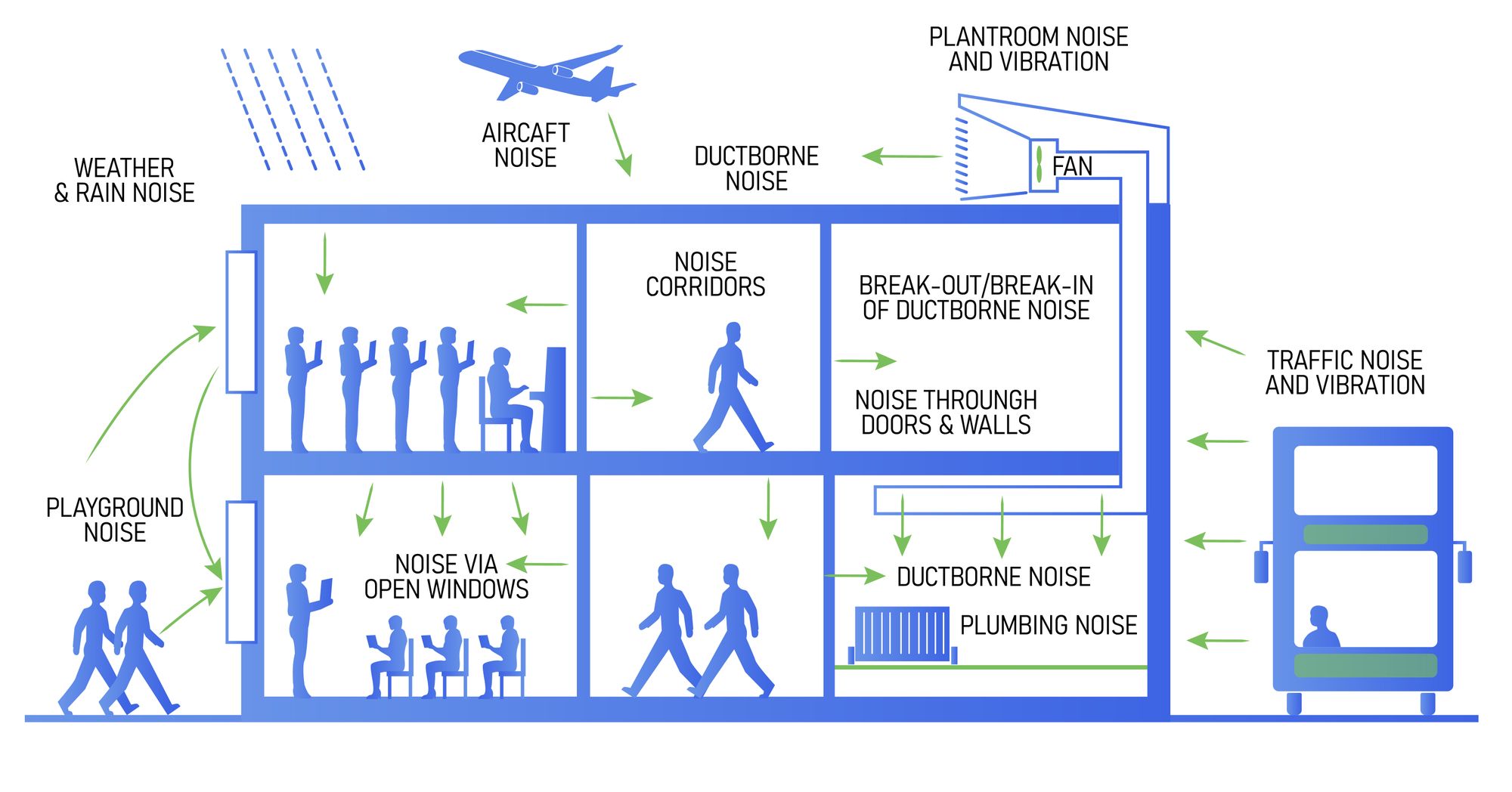
Outside noise at a school can include:
- Traffic
- Playgrounds
- Aircraft noise
- Weather noise
Inside noise at a school can include:
- Equipment like ventilation machinery
- Plumbing noise
- Neighboring classrooms
- Noisy hallways
Equipment
Equipment noise can come from sources like:
- Heating equipment
- Ventilation equipment
- Air conditioning ducts, equipment, and units
- Plumbing equipment
These types of equipment exist in all schools and can generate high levels of background noise that influence overall noise levels in a typical classroom. Background noise makes teachers raise their voices to be properly heard by students, as well as influences how loud students speak to each other and the teacher.
Another consequence of machinery-generated high background noise levels is decreased attention from students and difficulties focusing in class.
The simplest solution to this problem is quieter mechanical equipment that generates lower levels of background noise. This can mean replacing older and louder equipment or designing school buildings with quieter equipment from the start.
Reverberation
In acoustics, reverberation represents how long a sound persists after it is produced. Reverberation is what happens when a sound is reflected by surfaces or objects until it is absorbed.
Reverberation time (RT) is how quickly sound pressure is reduced and it is critical in determining what is the decibel level of the noise in a typical classroom. It depends on the volume of the room, its surface materials, and its contents.
According to Building Regulations Bulletin 93, the maximum reverberation time for most classrooms is 0.6 secs for primary schools and 0.8 secs for secondary schools.
Large spaces like gymnasiums typically have longer reverberation times and smaller ones like classrooms are less reverberant. If a room has a longer reverberation time, it may make it more difficult for children to hear clearly over the background noise. On the other hand, rooms with short reverberation times limit reflections and can cause students at the back of the room to not hear clearly.
Neighboring Classrooms and Hallways
How loud a typical classroom is will also be affected by how loud neighboring classrooms and hallways are. If the teacher and the kids need to speak over loud background noises like children running and shouting in the hallway or in a nearby classroom, this will affect how loud their classroom is and disrupt their learning process.
The noise coming from neighboring spaces will mostly depend on the building materials used in the school. Older buildings made of brick or concrete tend to be quieter than more modern schools made of lightweight materials.
The rule of thumb to determine if a classroom is sufficiently isolated from other classrooms or hallways is to check if you are able to hear a TV placed in the classroom from the classroom next door or from the hallway.
Lighting
In some cases, the culprit for the loudness of the background noise in a typical classroom is not one you would expect, namely the light.
Some fluorescent lighting systems can get loud as they emit a constant noise. The easy solution for this is to replace or properly maintain older lighting systems to avoid them generating flickering and buzzing sounds.
HVAC
When it comes to mechanical equipment in a school, HVAC systems are usually singled out as the loudest. HVAC units and ducts can generate background noise that can become disruptive in a typical classroom.
The solution is to use modern and quieter equipment, reroute the HVAC ducts, or relocate the exterior units causing excess noise.
Background Noise in Classrooms
Background noise from outside or inside the classroom and adjacent areas can vary from 32 dBA to 67 dBA.
If we consider that the teacher’s voice is usually between 50-50 dB, such high levels of background noise will make it impossible for the teacher to be heard unless they raise their voice to make up for the background noise (to about 78 dBA).
Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR)
Signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) is a comparison that helps estimate how understandable speech is in a room. It is the decibel level of the speaker (in this case, a teacher), minus the decibel level of background noise. The signal-to-noise ratio is not constant and depends on where it is measured in the room.
The higher the signal-to-noise ratio is, the harder it will be for students to understand what the teacher is saying. Ideally, the S/N ratio should be less than +10 to +15 dB in a typical classroom (background noise should be under 45 dBA).
Recommendations for Noise Prevention in Classrooms
Now that we know what the decibel level of the noise in a typical classroom is, here is how teachers or schools can limit noise levels:
- Follow acoustic standards when building schools
- Limiting loud noise sources in classrooms
- Improving classroom acoustics
- Designing classrooms of appropriate sizes
- Installation of solutions for improved reverberation and sound absorption
- Add carpeting and curtains to classrooms
- Properly maintain mechanical equipment
- Installation of suspended acoustic ceiling tiles or sound-absorbent panels like cork boards
When designing or refurbishing schools, decision-makers should also follow LEED Acoustic Standards that target reverberation time, sound transmission, class, and background noise levels. LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) is a framework for healthier, more efficient, and cost-saving green buildings.
Test the DL of the Noise in a Typical Classroom with the Decibel Pro App
The easiest way to measure the decibel level of the noise in a typical classroom is to use a sound level meter app like Decibel Pro.
Decibel Pro is easy to use and convenient and shows instant readings of noise levels on the screen of your iPhone or iPad. All you need to do is download it to your device and it will give you the decibel level of the noise in a typical classroom in seconds.
Decibel Pro is ideal for measuring noise levels to avoid dangerous exposure and protect your hearing. It also comes with a reliable hearing test that can help you identify any hearing damage early on.
To learn more about the Decibel Pro app, click here.



