- What Decibel is Dangerous for Humans?
1.1 Safe Listening Time and Distance - Issues Dangerous Decibel Levels Can Cause
2.1 Health Problems
2.2 Concentration Issues - At What Decibel Can Noise Level Damage Your Hearing?
- Signs That Noise Is Too Loud
- Common Sources Of Dangerous Sound Levels
5.1 Everyday Activities
5.2 Events
5.3 Tools - How to Protect Your Hearing
- How To Know If You're Exposed To Dangerous Noise Levels
7.1 Decibelpro.App
We all know that loud noises can cause a wide range of negative effects. In general, sounds above 85 dB are considered harmful to human hearing and we should avoid prolonged exposure to them.
A lesser-known fact is that certain frequencies that we cannot even perceive can also harm our hearing.
Read on to find out about harmful sound frequencies and dangerous decibel levels. Plus, how to protect yourself against hearing damage and hearing loss.
What Decibel is Dangerous for Humans?
The decibel scale is used to measure sound pressure caused by sound waves. It goes below zero, but 0 dB is considered to be the threshold of human hearing.
To answer the question of what decibel is dangerous and requires hearing protection, let’s look at the decibel levels of common sounds:
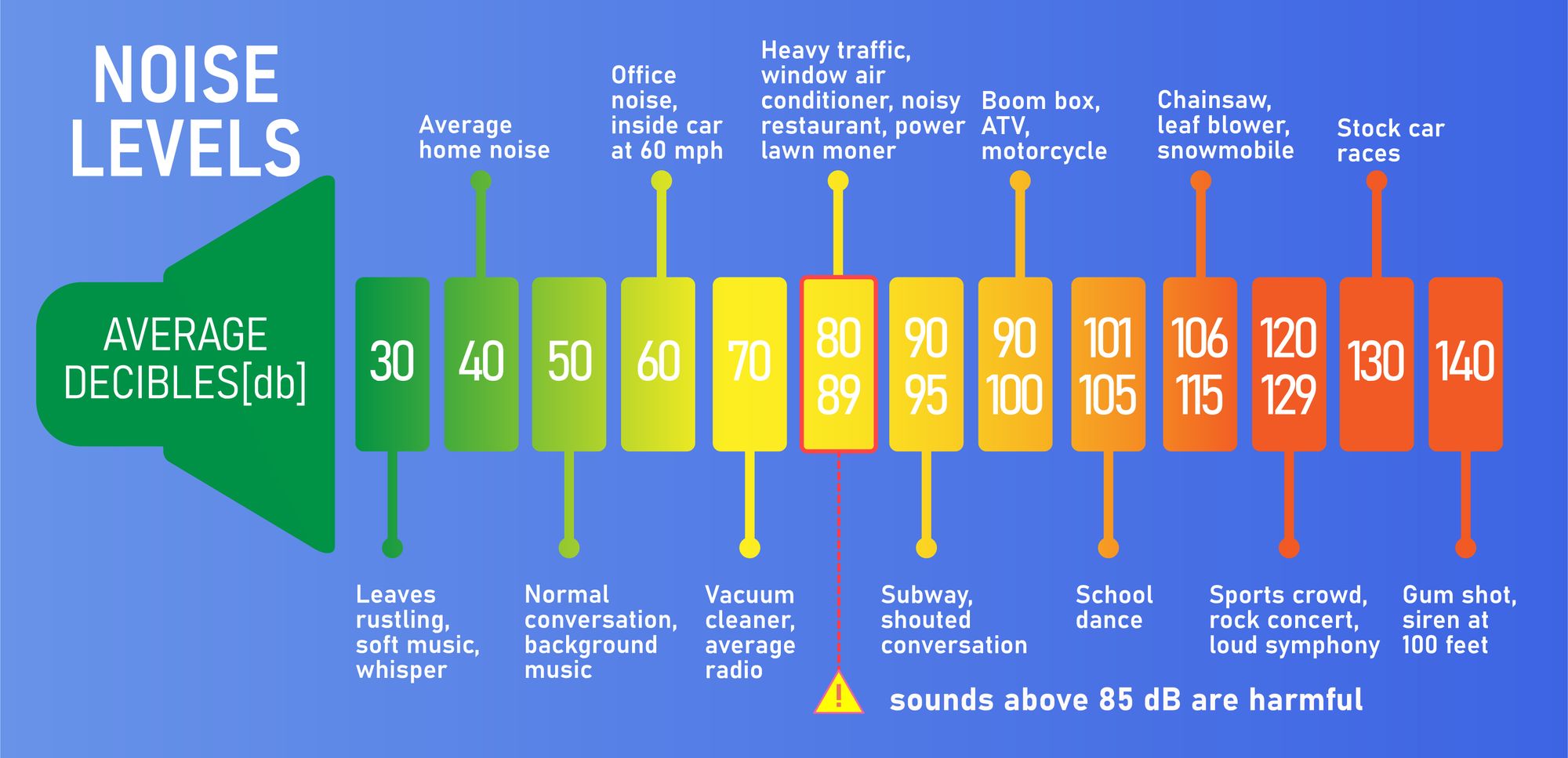

As indicated in the table above, a quiet room has an average dB level of 40, while a vacuum cleaner is above 70 dB. These values are under the recommended limit of 85 dB, so they are considered safe to human hearing.
On the other hand, a loud rock concert or a jackhammer both exceed the recommended limit of 85 dB. Impulse noise with high decibel levels such as firecrackers or gun blast are also very dangerous. Consequently, you should avoid extended exposure to decibel levels above 85 dB.
In addition to decibel levels, harmful sound frequencies can also be damaging to human hearing. Low frequencies (under 20 Hz) and high frequencies (above 20,000 Hz) that humans cannot perceive can also affect the ear and have adverse effects on our health.
Safe Listening Time and Distance
The general rule is that sounds above 85 dB can cause permanent hearing damage or noise-induced hearing loss. However, it all depends on how long you are exposed to the said dangerous decibel levels.
Here is a table showing harmful decibel levels and the related maximum exposure time:
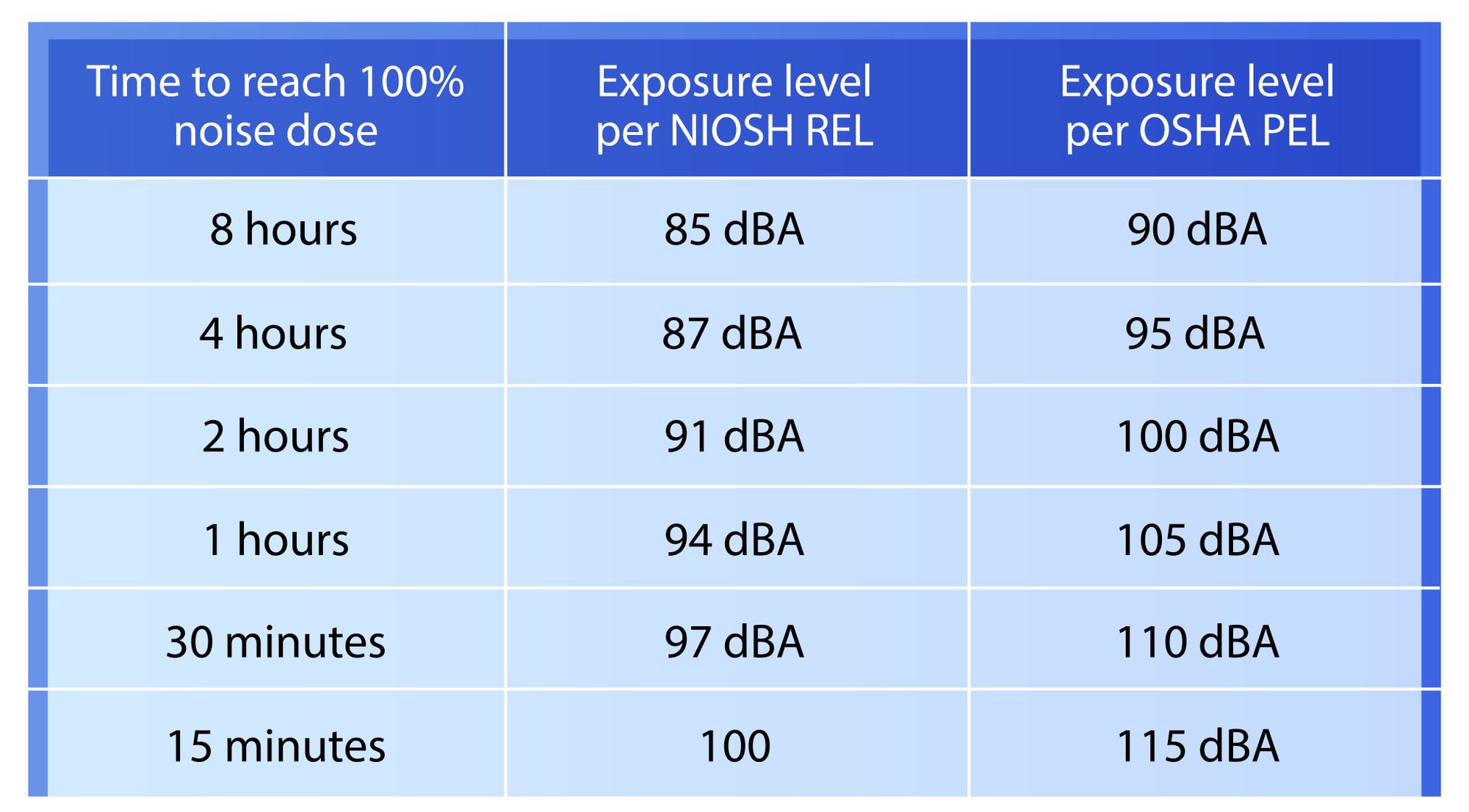
Distance also plays an important role. The further you are from the noise source, the lower the perceived decibel level. Therefore, the safer you will be from dangerous decibel levels.
Distancing yourself from the noise source is a good way to protect your hearing. For example, if you are at a concert, you should stay further away from the speakers to reduce risks.
Issues Dangerous Decibel Levels Can Cause
The eardrum is very sensitive to loud noises and this can lead to negative effects on your hearing. However, dangerous decibel levels can harm more than just your hearing.
Extended exposure to loud noise is linked to various health issues ranging from tinnitus to high blood pressure or heart rate.
Health Problems
Exposure to harmful sound frequencies and dangerous decibel levels is linked to the following health problems:
- sleeping disturbance
- elevated stress levels
- migraines
- peptic ulcers
- hearing impairment or damage
- tinnitus
- hypertension
- vasoconstriction
- heart diseases and diabetes
- immune system issues
- noise-induced hearing loss
Concentration Issues
Depending on how sensitive you are, noise levels don’t need to be very high to cause concentration issues.
According to specialized studies, concentration levels can also drop dramatically due to low-level background noise. This frequently occurs in environments such as offices, schools or at home.
Effects of background noise include excess cortisol release and decreased dopamine levels.
Excess cortisol negatively impacts:
- thinking
- planning
- retaining information
- reasoning
- impulse control
Dopamine availability negatively impacts:
- brain function
- learning ability
- memory
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health says that continued exposure to ambient noise can also increase stress levels and increase risks related to numerous illnesses.
At What Decibel Level Can Noise Damage Your Hearing?
Noise exceeding 85 decibels can damage your hearing.
To protect your hearing, you need to learn the signs indicating that noise is too loud and avoid exposure to common sources of dangerous sound levels.
Signs that Noise is Too Loud
- The sound causes your ears to hurt.
- You must raise your voice to be heard when you talk.
- You have difficulty hearing a person next to you talk because of the sound.
- Once you leave the nosy area, other sounds seem muffled.
- Your ears are ringing after hearing the sound.
Common Sources of Dangerous Sound Levels
While most of us are aware and try to stay away from dangerous noise sources, we may often ignore some common sources that can be harmful to our hearing.
Everyday activities such as listening to music on our headphones, concerts, or using power tools can all exceed recommended noise limits.
The table below shows some common examples:
|
Common activities |
Events |
Power tools or machinery |
|
|
|
Everyday Activities
Here are the decibel levels of some common, day-to-day activities:
- Using the washing machine/air conditioner: 50 – 75 dB
- Using the vacuum cleaner: 60 – 85 dB
- Drying hair with a hairdryer: 60 – 95 dB
- Watching TV: 70 dB
- Ringing doorbell or telephone: 80 dB
- Baby crying: 110 dB
- Holding a squeaky toy close to the ear: 110 dB
Events
Here are the decibel levels for common events:
- Percussion section at symphony: 130 dB
- School dance, boom box: 100 dB
- Symphony concert: 110 dB
- Rock concert: 110 -120 dB
- Football game (stadium): 117 dB
- Band concert: 120 dB
- Stock car races: 130 dB
Tools
Here are the decibel levels for common tools:
- Factory machinery: 100 dB
- Snow blower: 105 dB
- Power saw: 110 dB
- Leaf blower: 110 dB
- Chain saw: 120 dB
- Pneumatic drill: 120 dB
- Chain saw: 125 dB
- Jackhammer: 130 dB
How To Protect Your Hearing
Hearing protection solutions include earplugs and earmuffs. They come in different shapes and sizes and have various features. They all have a Noise Reduction Rating (NRR) showing their effectiveness.
Another efficient way to protect your hearing is to:
- avoid exposure completely
- limit exposure (in time)
- distance yourself from the sound source.
How to Know If You Are Exposed to Dangerous Noise Levels
You need to be aware of your surroundings and watch out for warning signs to keep your hearing safe. The best thing to do is to monitor noise levels in your workplace, home, and other environments.
Whenever noise levels exceed 85 dB, remove yourself from that environment or distance yourself from the sound source.
If you cannot avoid exposure, ensure that you have hearing protection such as earmuffs or earplugs. They can help prevent hearing damage or loss.
Decibel Pro App
The Decibel Pro app is a convenient way to monitor noise levels and keep your hearing safe wherever you are. Simply install it on your phone or tablet and use it to get professional sound level meter readings whenever you need to.
Open Decibel Pro, place it as close as possible to the noise source and see the decibel level on the screen.
To learn more about the Decibel app, click here.