- What Is 60 Decibels
- How Loud Is 60 Decibels
- What Does 60 Decibels Sound Like
- Can It Damage You Hearing
- When Hearing Protection Is Required
5.1 You're Exposed To Loud Sound
5.2 You're Close To The Sound Source
5.3 You Are Exposed To It For A Long Time - 60 dB Comparison To Other Intensities
- How Can I Measure Noise Level
You’ve most likely heard about sound being measured in decibels. And about decibel levels and dangerous noise. But the best way to understand sound measurement and potentially hazardous decibel levels is to put things in a practical light.
For instance, let’s take 60 decibels. It’s a value that sits right between no sound at all and the pain threshold. So, how loud is 60 decibels really? What does 60 dB sound like? Read on because that’s exactly what you’ll find out in this article.
What Is 60 Decibels?
To answer the question ‘What is 60 decibels?’, let’s clarify what a decibel is. Decibel is the measurement unit used for indicating the intensity of a sound as perceived by the human ear. The more intense a sound is, the higher up it will be on the decibel scale.
The human ear perceives a wide range of sounds. 0 dB is considered the threshold of human hearing and 120-140 dB is considered the threshold of pain. That means a sound so powerful, it will make your ears hurt.
60 decibels is right in the middle of this range between no sound at all and painfully intense sound. 60 dB is the equivalent of a normal conversation level.
How Loud Is 60 Decibels?
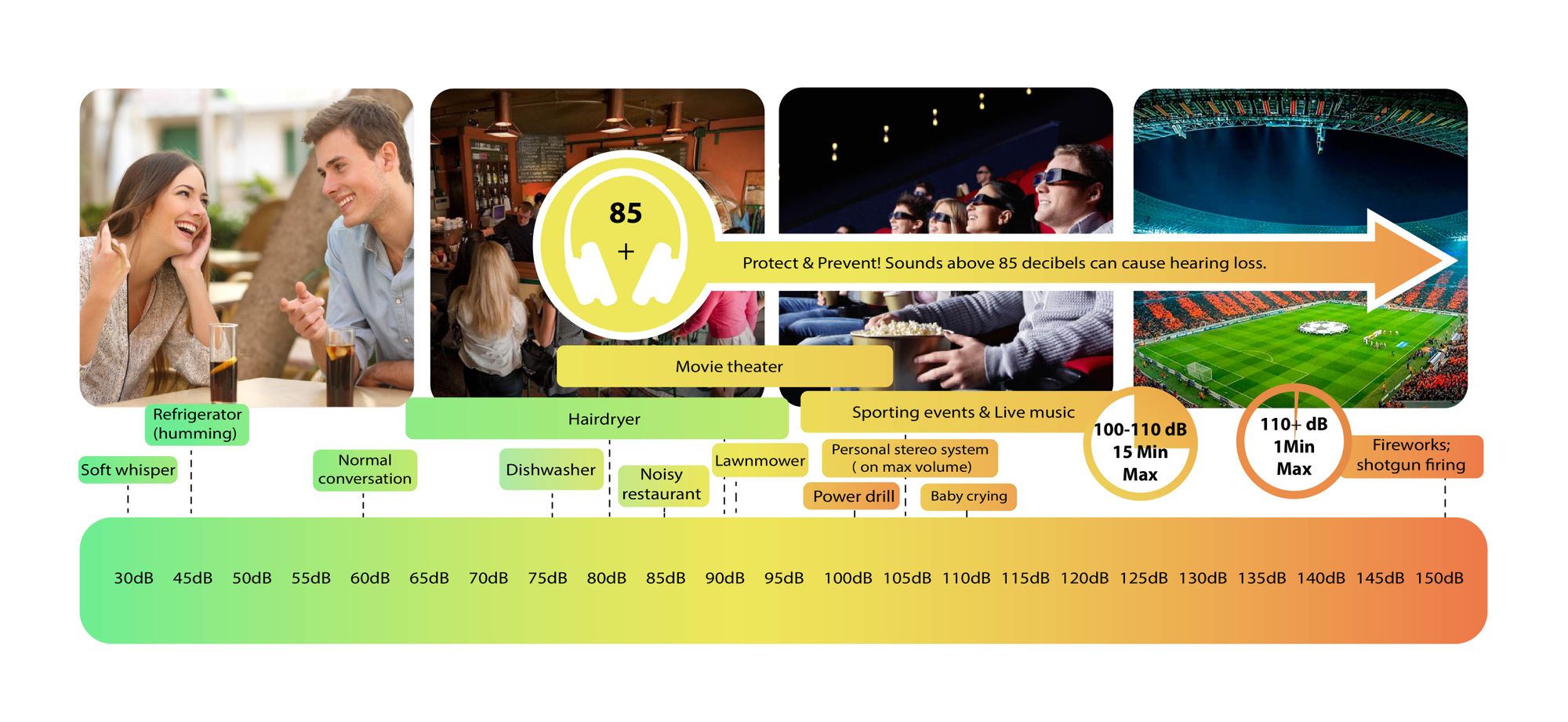
60 decibels is as loud as a normal conversation between two people sitting at a distance of about one meter (3 ¼ feet). It is the average sound level of a restaurant or an office. 60 decibels is considered a safe sound level for human hearing as it is under the generally accepted limit of 85 dB that is considered dangerous.
For comparison, other common decibel levels are:
- Normal breathing — 10 dB
- Ticking watch — 20 dB
- Normal rainfall — 35 dB
- Refrigerator hum — 40 dB
- Air conditioner — 60 dB
- Washing machine — 70 dB
- Traffic (inside car) — 80–85 dB
- Lawnmowers — 80-85 dB
However, the answer to ‘How loud is 60 decibels?’ is a little more complex than that.
To understand how loud 60 dB is, we need to look at how the decibel scale works. It is not a linear scale, but a logarithmic one. This means that if 0 dB represents no sound at all, then 10 dB represents a sound that is 10 times louder. Now, a 20 decibels sound is 100 times more intense than 0 decibels. And so on until a 100 decibels sound is one billion times more intense than complete silence (0 decibels).
So, while a sound at 60 decibels is 10 times louder than one at 50 decibels, it is also 100 times louder than a sound at 40 decibels and 1000 times louder than 30 decibels.
What Does 60 Decibels Sound Like?
It’s difficult to explain what does 60 decibels sound like because not all sounds are the same. And how loud we perceive a sound to be depends on several factors.
The intensity of a sound as you perceive it depends on its source, your distance from the source, and the duration of your exposure to that sound.
For example, let’s take the sound of a washing machine at 60 decibels. It is not the same as the sound of people talking at 60 decibels. The first one is a constant sound, while the second is fluctuating.

Next, while the washing machine generates a 60 dB sound, you will perceive the intensity of that sound depending on how far away you are from it. If the washing machine is close to your ear, you will perceive the sound as loud. If you are in the other room, you will barely hear it.
How loud 60 decibels is also depends on how sensitive a person is to certain sounds.
For example, a 60 decibels sound level like the one you would find in an office can be considered normal. Or, it can cause annoyance, affect concentration, and raise blood pressure.
The reason for this is that some people are negatively affected by the fluctuating nature of certain sounds. Like the sound of people talking.
Second of all, hearing others talk can be very distracting. Even if we want to not focus on what they are saying, we cannot resist it because that’s what we are programmed to do: to listen to others.
So, in this case, the 60 decibels sound level caused by people speaking to each other or on the phone can be considered loud by some.
Can It Damage Your Hearing?
Hearing damage can occur when loud noise affects the inner ear (cochlea), damaging the cells and membranes.
Hearing damage can be caused by exposure to an extremely loud sound for a brief period or exposure to loud sounds for a longer time. Hearing damage can be temporary or permanent and can lead to noise-induced hearing loss.
Exposure to sound levels above 85 decibels for more than 8 hours per day is considered dangerous to human hearing. At the same time, short-term exposure to extremely loud sounds (above 120 dB) like an explosion is considered likely to damage your hearing immediately.
60 decibels is considered a moderate and safe sound level, unlikely to damage your hearing.
When Hearing Protection Is Required
Hearing protection devices are designed to protect your ears and minimize the damaging effects of loud sounds.
How likely a sound is to damage your hearing depends on how loud the sound is, how far away it is and how long you are exposed to it.
You're Exposed to Loud Sound
You should wear a hearing protection device such as earplugs or earmuffs whenever you are exposed to loud sounds. Sounds exceeding 85 decibels are considered dangerous to human hearing, especially if your exposure to these sounds exceeds 8 hours per day.
You could be exposed to loud sounds if you:
- work in factories or construction
- are using power tools
- attend concerts or sporting events
- are exposed to intense sounds caused by explosions, gun blast, firecrackers

The rule of thumb is that if you are having difficulty talking or hearing others talk over the sound, it is too loud. In these cases, you should wear hearing protection or move away from the sound source.
You're Close to The Sound Source
How likely a sound is to be damaging to your hearing depends on your distance from the source. The closer you are to the sound source, the louder you will perceive the sound.
For example, if you are attending a concert, you should wear hearing protection if you are standing close to the speakers. At the same time, you can also protect your hearing by moving away from the sound source.
You Are Exposed to It for a Long Time
Hearing damage occurs when the intensity of the sound is extreme or when the intensity is moderate, but the exposure time is long. This means you should wear hearing protection when you are exposed to sounds above 100-110 dB for any period exceeding 15 minutes or sounds above 85 decibels for over 8 hours.
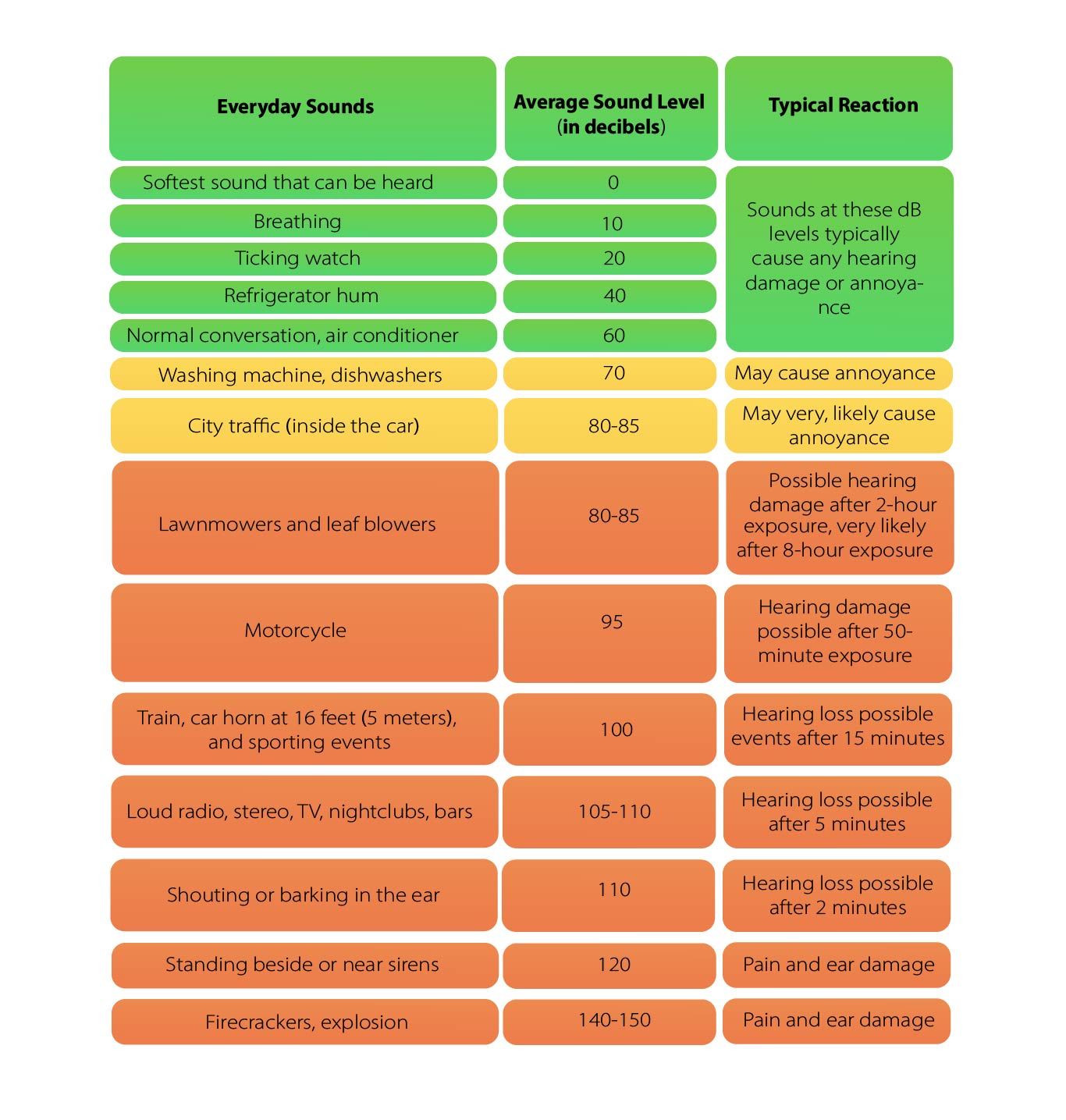
60 dB Comparison to Other Intensities
To better understand how loud is 60 decibels, here is a table showing common dB levels of everyday sources:
How Can I Measure the Noise Level?
You can use a sound level meter to measure noise levels. They are hand-held devices that use an external mic to capture sound and measure decibel levels. However, they can be quite expensive.
A more convenient way to measure sound is using a sound level meter app that you can download on your smartphone or tablet.
DecibelPro.App
Decibel Pro is an app that offers professional-grade sound level measurements. You can use it to measure noise levels around you whenever you think you may be exposed to loud noise and it also has a feature calculating your daily exposure according to NIOSH and OSHA standards. This way, you can easily prevent and avoid hearing damage or hearing loss.
To learn more about the Decibel app, click here.



