- What Is 55 Decibels?
- How Loud Is 55 Decibels
- What Is 55 Decibels Of Sound
3.1 Noise sources that contain 55 dB - How Loud Is 55 Decibels In Music
- What Is 55 dB Compared To
5.1 50 Decibels
5.2 60 Decibels
5.3 70 Decibels - Is 55 dB Acceptable Or Unacceptable For Human
- Main Rules For Noise Prevention
- Learn More About dB With Decibelpro.App
From the lowest sounds perceivable to humans (0-10 dB) to those that can cause instant hearing loss (120-140 dB), we use the decibel scale to define loudness. Decibel levels vary depending on the intensity of a sound and all sounds have specific decibel levels.
In this article, we’re going to explain how loud is 55 decibels, if it is too loud, or if it falls within the limits of hearing safety recommendations. Read on to learn all about it.
What Is 55 Decibels?
55 dB is a decibel level assigned to moderate sounds like the sound of a normal conversation or that of music playing in the background. On the decibel scale, it is in the lower range.
Considering that 0 dB is the threshold of human hearing, and 120-140 dB is the threshold of pain, sounds reaching 55 dB are considered mild and not harmful to human hearing.
Below you can find a graphic listing decibel level thresholds as well as examples of common sounds of different intensities:
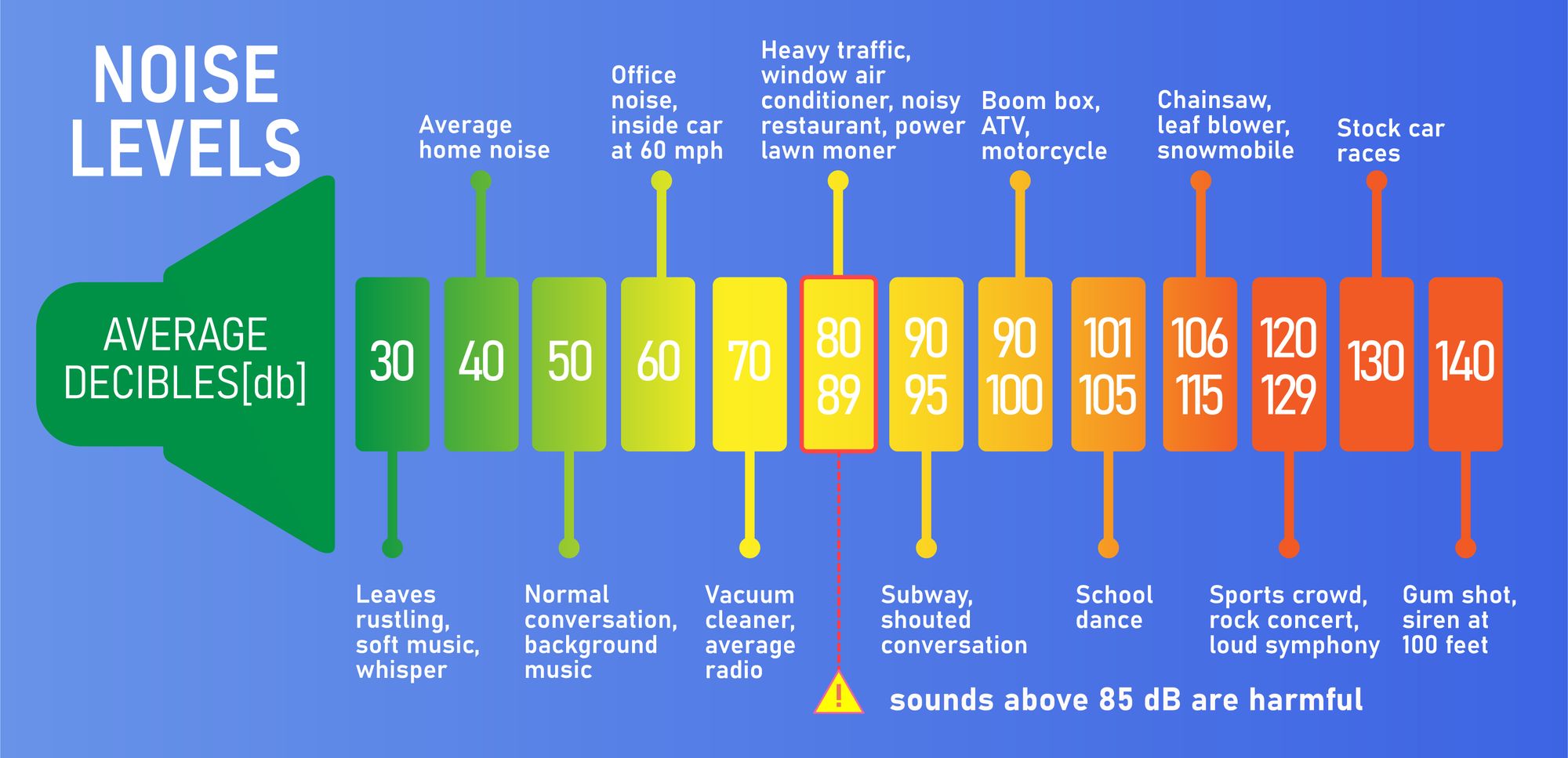
How Loud Is 55 Decibels?
55 dB is a level that describes moderate to soft sounds. In fact, it is comparable to a quiet home environment, a residential street, or a normal conversation between two people. Since it is under 70 dB, it is not considered a harmful noise level.
All sounds under 70 dB are considered safe for human hearing according to the Environmental Protection Agency. According to EPA recommendations, keeping your noise exposure under 70 dB over a period of 24 hours can help you prevent noise-induced hearing loss or hearing damage in the long term.
According to the World Health Organization’s Guidelines for Community Noise, 55 dBA is a daytime noise level that people normally do not find disturbing or annoying.
What Is 55 Decibels of Sound?
55 decibels is a sound level that is almost 18 times louder than a soft whisper (30 dB) and 180 times louder than a leaf rustling (10 dB). However, it is also 18 times softer or less loud than an average rock concert, a lawnmower, or a scream (90-110 dB).
On the other hand, your distance from the source will also affect how loud a sound is. If you are standing right next to the sound source, you will perceive the sound as loud as it is. But, if you move further away, it will sound softer even though it does not decrease in intensity. The only thing changing is how close you are.
Noise Sources That Contain 55 dB
If we want to define how loud is 55 decibels, let’s take some examples. It is a sound level equal to that of:
- A normal conversation
- An electric kettle
- A residential street
- A radio playing music in the background
- An electric fan
- An office reception area
- A moderately quiet home
- An electric toothbrush
How Loud Is 55 Decibels in Music?
If you are listening to music on your iPhone headphones, for example, 55 decibels would be at about 53% of the volume. This level is considered safe as the golden rule is to not exceed 60% of the volume for longer than 60 minutes at a time.
When it comes to music, you may perceive it as louder than it is. If a sound is continuous or steady, you perceive it softer than an irregular one. And since music is made up of many different sounds, it may, in fact, sound louder to you than a common sound of the same dB level.
If you are listening to music in the background between 45 and 56 decibels, this is an acceptable level when performing a repetitive task that doesn’t require much concentration. On the other hand, if you are trying to study or work on something important, this level of music may become disruptive or annoying.
What Is 55 dB Compared To
To determine what is 55 decibels, let’s look into a dB comparison.
Keep in mind that, on the decibel scale, each time a sound increases by 3 decibels, it doubles its intensity. And each time it increases by 10 dB, it multiplies its intensity by 10.
50 Decibels
A sound that is 55 decibels is 3.17 times more intense than a sound that is 50 decibels.
60 Decibels
Compared to a 55 dB sound, a 60-decibel sound is 3.17 times more intense.
70 Decibels
When it comes to 70 decibels, the 15-decibel difference when looking at the intensity is even higher. In this case, the 70 dB is 31.6 times louder than the 55 dB.
Is 55 dB Acceptable or Unacceptable for Humans?
55 dB is considered acceptable for humans. It is a safe noise level under the levels that are considered unacceptable (<70 dB for more than 24 hours or <85 dB for over 8 hours/day).
Main Rules for Noise Prevention
For noise-induced hearing damage prevention, you should limit your exposure to loud noise and protect your hearing with specialized gear.
The main rules to follow when noise levels exceed 85 decibels are:
- Move away from the sound source
- Limit your exposure depending on the noise level
- Use earplugs, ear muffs, or noise-canceling headphones
- Check your hearing regularly (at home, get an audiogram, or visit an ENT doctor for a screening)
- Monitor the after-effects of exposure to loud noises
- Monitor your surroundings and identify sources of potentially dangerous noise
Learn More About dB with DecibelPro.App
The easiest way to check the loudness of a sound is to use a sound-level meter app like Decibel Pro.
The app works just like a professional sound level meter and instantly measures noise levels, displaying the results on your screen. To use it, download it to your iPhone or iPad from the AppStore.
For noise-induced hearing damage prevention, you should limit your exposure to loud noise and protect your hearing with specialized gear.
The main rules to follow when noise levels exceed 85 decibels are:
- Move away from the sound source
- Limit your exposure depending on the noise level
- Use earplugs, ear muffs, or noise-canceling headphones
- Check your hearing regularly (at home, get an audiogram, or visit an ENT doctor for a screening)
- Monitor the after-effects of exposure to loud noises
- Monitor your surroundings and identify sources of potentially dangerous noise
To learn more about the Decibel app, click here.



