- At What Decibel Is Hearing Protection Required
- What Effects High Noise Levels Can Have
2.1 Health Issues
2.2 Lower Productivity And Efficiency - When Is Hearing Protection Required At The Workplace
3.1 Employees Are Exposed To Workplace Noise
3.2 If Employee Has Not Yet Had A Baseline Audiogram Established
3.3 An Employee Has Experienced A Standard Threshold Shift - When Should Hearing Protection Be Worn In Everyday Life
- Best Devices To Protect Hearing
5.1 Earplugs
5.2 Earmuffs - When Is Double Hearing Protection Required
6.1 What Is Double Protection
6.2 Who Should Use It - Find Out The Noise Level Around You Now With Decibelpro.App
Hearing protection is essential in certain environments. Employees in industrial and construction environments in particular are exposed to hazardous levels of noise.
For this reason, hearing protection regulations and norms are put in place all around the world. Their main goals are hearing conservation and the protection of workers.
Excessive noise, however, may also occur in other environments. Some of which may not be regulated. In such situations, it’s up to each of us to use hearing protection devices to avoid hearing damage or hearing loss.
Read on to find out at what decibel level is hearing protection required and when is double hearing protection required.
1. At What Decibel Level is Hearing Protection Required?
The official answer to ‘How loud is too loud?’ is 85 dB for 8 hours per day. This is the general limit of decibels from which hearing protection is required. Most health and hearing protection organizations recommend it.
Still, when it comes to hearing protection, things are not so straightforward. The chart below can help you visualize some common decibel levels:
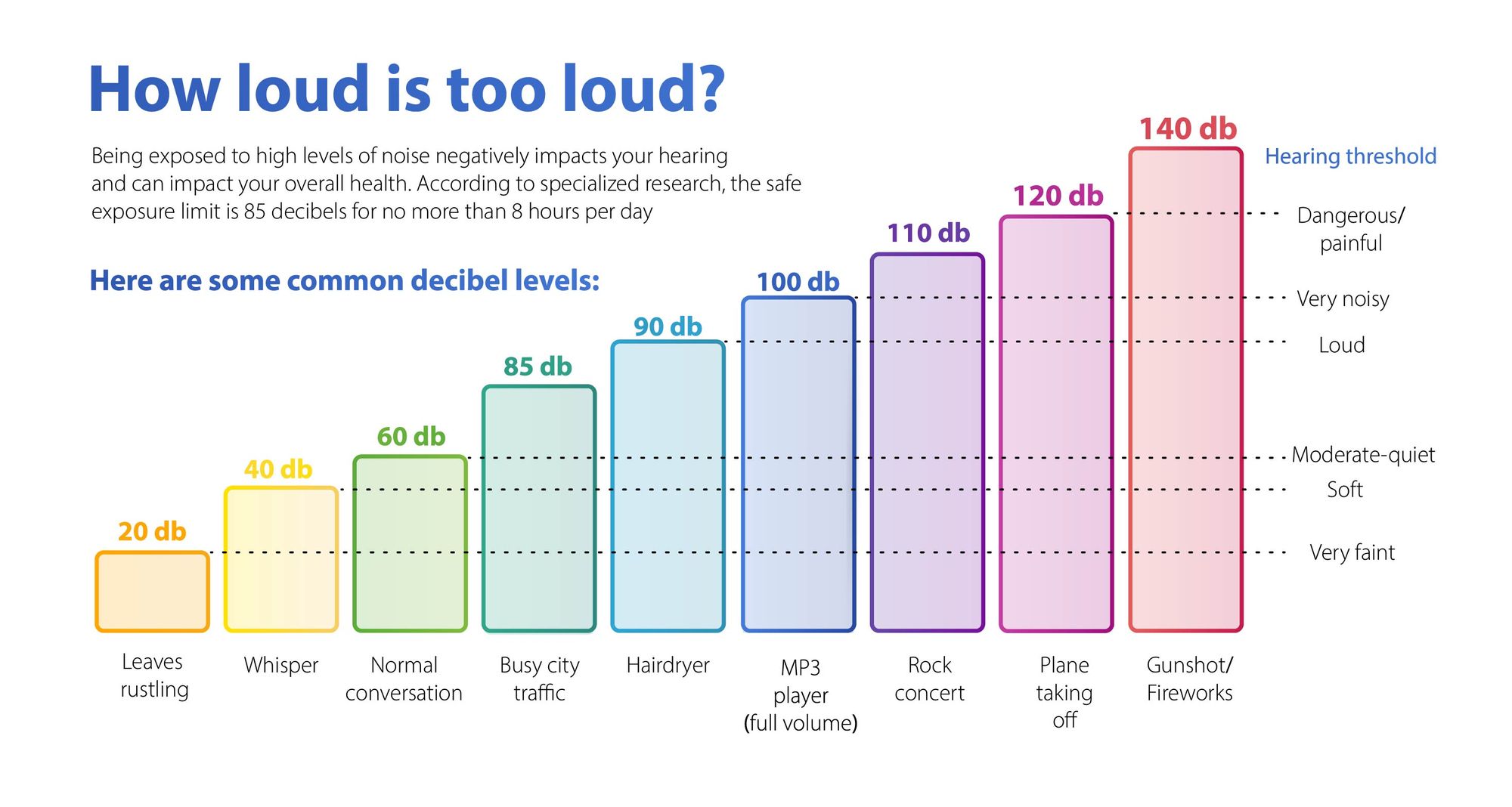
As you can see, the difference between moderately quiet and very noisy is not as much as you would think. For instance, you probably wouldn’t consider playing your mp3 player loud as hazardous to your hearing. Still, it is.
However, you should always follow this simple rule:
Whenever the noise level is making it difficult for you to hear someone speaking to you from about 3 feet, you need hearing protection.
You need hearing protection in industrial environments or construction sites. Or, if you use tools such as:
- lawnmowers
- tractors
- chainsaws
- hammer drills
- power saws., etc.
To properly determine when hearing protection is required, exposure time is also very important.
Here are some common examples of decibel level and recommended maximum exposure:
- 85 dB - 8-hour exposure limit (according to OSHA)
- 100 dB – 15-min exposure limit
- 110 dB – 1-min exposure limit
2. What Effects High Noise Levels Can Have
Excessive noise levels can have many adverse effects on our health. They range from a simple ringing in the ear to hearing loss or even heart disease or diabetes.
In some instances of exposure to high noise levels, simple hearing protection is all it takes to stay safe. Extreme cases are the ones when double hearing protection is required.
Health Issues
There are many health issues related to exposure to harmful noise levels. The most common are:
- tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- hearing damage
- noise-induced hearing loss
Other noise-related health issues include:
- migraines
- hypertension
- vasoconstriction
- heart disease
- diabetes
Lower Productivity and Efficiency
High noise levels can also cause concentration issues. In turn, these can cause low productivity and efficiency levels.
The reason for this is that noise can lead to an increase in cortisol levels and a drop in dopamine levels. This affects cognitive functions such as:
- thinking
- retaining information
- learning or memory abilities
Specialized studies have found that concentration levels can also drop due to low-level background noise (offices, schools, or at home).
3. When is Hearing Protection Required at the Workplace?
There are several circumstances when hearing protection is required at the workplace. General regulations and recommendations exist. On top of those, most employers in industrial/construction environments have their specific and more strict rules. They set at what decibel hearing protection is required for their employees to additionally protect them.
There are several circumstances when hearing protection is required in workplaces. Here are a few examples:
When Employees are Exposed to Workplace Noise
OSHA (the US Occupational Safety and Health Administration) requires employers to constantly monitor noise levels in certain industries.
In industrial and maritime environments and construction sites, employers must implement hearing conservation programs whenever noise levels exceed 85 dB on an 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA).
Here are the OSHA permissible noise exposures:
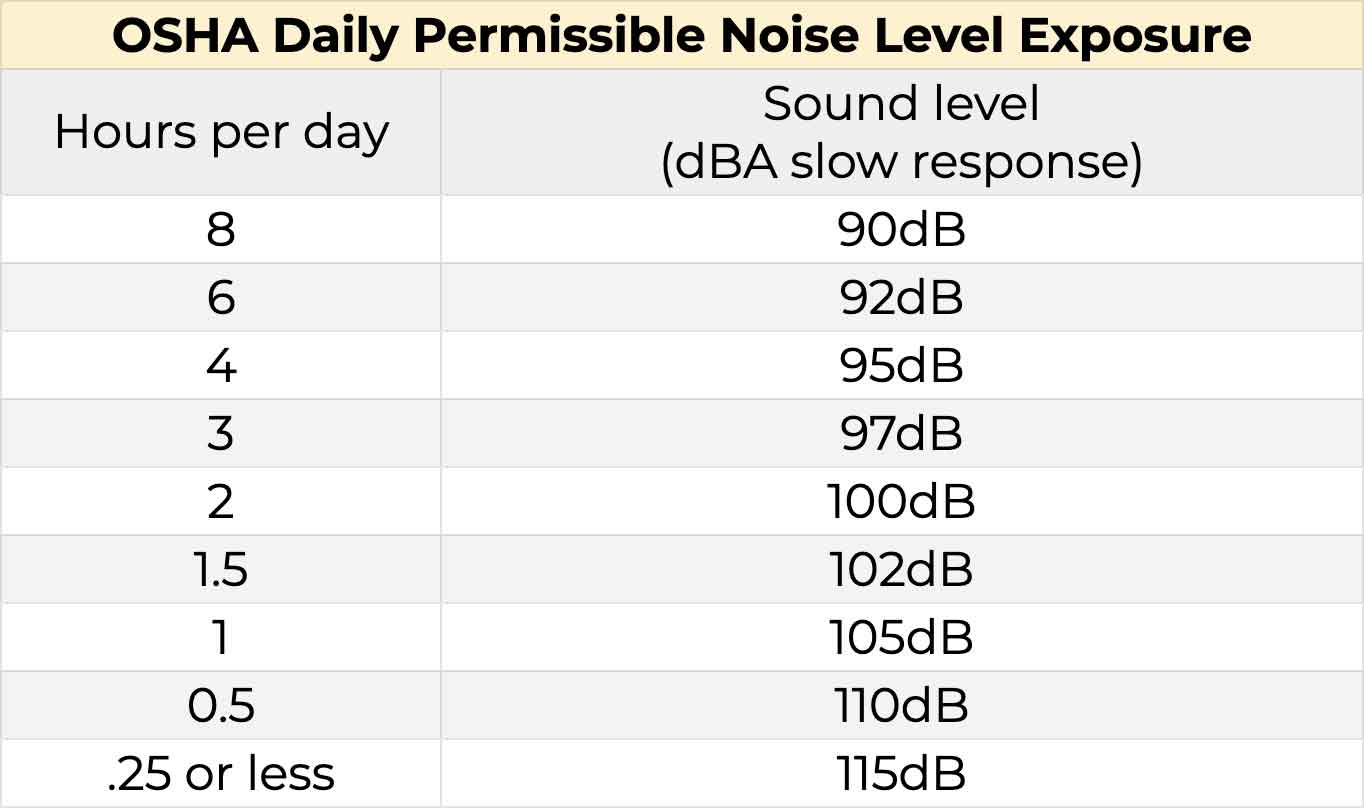
The main purpose of hearing conservation programs is to prevent occupational hearing loss, preserve and protect workers’ hearing. They include equipping workers with information as well as hearing protection devices like earmuffs or earplugs.
If an Employee Has Not Yet Had A Baseline Audiogram Established
A baseline audiogram is an audiogram given to an employee before or after their first exposure to noise above the action level. This is an OSHA requirement.
Hearing protection is mandatory until the employee’s baseline audiogram is performed.
Baseline audiograms are used as reference against future audiograms and determine if and how bad an employee’s hearing is deteriorating over time.
When an Employee Has Experienced a Standard Threshold Shift
Workers in environments with high noise levels are tested annually according to federal hearing conservation standards. Their annual tests are compared with the baseline hearing threshold levels obtained when they started the job.
According to current OSHA hearing conservation standards, an audiogram reviewer identifies a Standard Threshold Shift when the baseline audiogram hearing threshold changes by an average of 10dB or more at 2000, 3000, or 4000 Hz in either ear.
These periodic tests allow employers to monitor any changes in the baseline data and determine if additional steps are required to protect an employee’s hearing. Additional steps are implemented when a standard threshold shift occurs to prevent any further progression of hearing loss.
Additional steps may include:
- improving the fit of hearing protection devices
- reinstructing the worker on hearing loss risks
4. When Should Hearing Protection Be Worn in Everyday Life?
You should wear hearing protection whenever you are exposed to noise levels above 85 dB. This is applicable no matter if you are in a work or home environment.
The best way to prevent noise-induced hearing loss is to move away from the source. Or, to eliminate it entirely. If that is not possible, use devices like earplugs or earmuffs.
If your everyday life includes work in a noisy environment, make sure your employer implements proper hearing conservation programs. These programs include:
- noise assessment
- implementing methods for controlling noise levels
- advice on hearing protector selection
- employee training and education
- audiometric testing
- environment inspection and monitoring (with dosimeters)
- program evaluation
At home, you can protect your hearing by wearing hearing protection devices whenever you use power tools or machines.
You can also avoid listening to loud music for extended periods and turn down the volume on your mp3 player or TV. Many people disregard the loudness of usual home entertainment systems and don’t realize that they can be harmful.
Your hearing protection should:
- have appropriate efficiency for the environment/noise level they are used in
- provide adequate protection (check specifications)
- be compatible with other required personal protective equipment or communication devices
- fit tightly but be comfortable
- allow you to hear alarms or warning sounds
5. Best Devices to Protect Hearing
Fortunately, there are several hearing protection devices that can help you maintain your hearing health and avoid hearing damage or hearing loss.
You should always wear the type of hearing protection that suits the decibel levels you are exposed to. For instance, if decibel levels are between 80-95 dB, you can wear earplugs or earmuffs. Decibel levels above 100 dB is when double hearing protection is required.
Earplugs
Earplugs are hearing protection devices you insert in your outer ear canal. Their efficiency depends on how well the earplugs block the ear canal. They must have an airtight seal.

Earplugs come in all shapes and sizes for different ear canals. Some find them hurtful, which is why they can also be custom fitted.
Earmuffs
Earmuffs form an air seal by covering the entire outer ear, blocking the ear canal and the sound waves. They are held in place by a band that you can adjust to keep them firmly around the ear.

They are considered more efficient than earplugs.
6. When is Double Hearing Protection Required?
Double hearing protection is recommended when noise levels exceed 100-105 dB.
What is Double Hearing Protection?
Double hearing protection refers to wearing two hearing protection devices at once.
Usually, the two devices worn together are an earplug-type protector and a headset type of protector. One is inserted in the ear canal and the other covers it.
While it may not be very comfortable, double hearing protection is very efficient. It can reduce noise levels dramatically and help prevent hearing damage or hearing loss.
Who Should Use It?
Double hearing protection is not included in the OSHA rules and regulations as a requirement.
However, certain industries have specific guidelines making double hearing protection a requirement for the workers’ safety.
For example, the Mine Safety & Health Administration (MHSA) requires miners to wear double hearing protection when noise levels exceed 105 dB.
At the same time, the advisory and research board behind OSHA recommends that workers in environments with noise levels above 100 dB wear double hearing protection.
In Europe, double hearing protection is recommended when the residual level at the ear is above the European Directive limit on noise. That is 87 dBA for 8 hours or 140 dBC at peak sound pressure.
7. Find Out the Noise Level Around You Now with Decibel Pro App
In regulated environments, noise levels are monitored with specialized tools called dosimeters.
However, you now have the option of easily checking noise levels yourself with a sound level app. Decibel Pro offers instant noise level readings and a dosimeter feature (complete with OSHA and NIOSH standards) right on your smartphone or tablet.
All you have to do is download it, open it, and see the professional-grade readings right on your screen. You can also use it to record noise levels and share them with others.



